The entry door in the house I live has an automatic door closer, which started to close the door faster and faster over time and slammed the door with an incredible sound. There is the possibility to to adjust closing speed with two screws on the door closer for the overall closing speed, and the speed for the final few degrees.
As tuning the system with the screws is quite difficult (a few degrees of turning the screws changes closing times by 10 secs), I added a speed recording device temporarily to the door and recorded the closing speed. And I wanted to use the wireless capabilities of the MKR100 to avoid having a lot of cables in a public area.
The door angle was measured with a simple potentiometer, uses the ADC in the MKR1000 processor and sends the measurement values with a rate of 100 samples per second to a host computer.
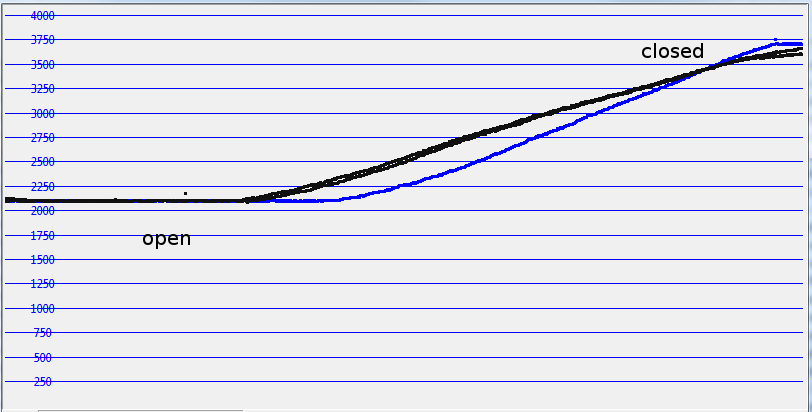
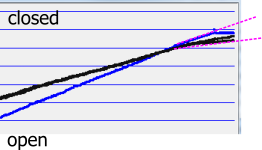
The chart shows in blue the original closing action, in black the last two records. Horizontal axis is time. The ascending slope is decreased on the black lines, indicating lower speed. And especially the last few degrees move slower and avoid the ‘big bang’ of the door.
The measurement device is temporarily clipped to the door.
The acryl rod with the small parallel vice form the anchor point for the potentiometer.
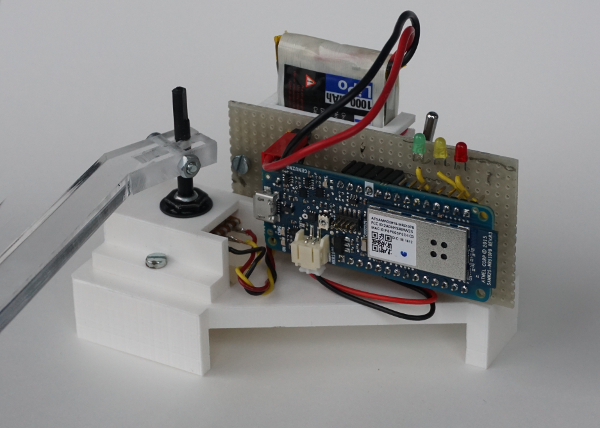
A closeup of the device shows the details
- the MKR100 is mounted on a prototyping board.
- Three LED display wireless connection status ‘connect to access point’, ‘access to socket’, ‘operational’.
- The LiPo battery is on the back.
- The adapter is 3d-printed.
On the host computer, a python program opens a socket and receives the data. With TKinter, the data are displayed.